08.CentOS7学习笔记–Shell脚本实例
Shell 脚本学习推荐网站
| [Shell 教程 | 菜鸟教程](https://www.runoob.com/linux/linux-shell.html) |
LinuxCommand.org: Writing shell scripts.
Shell 脚本实例
Shell 脚本使用
赋予执行权限
chmod +x ./01-helloworld.sh
chmod +x ./02-array.sh
chmod +x ./03-if.sh
chmod +x ./04-while.sh
chmod +x ./05-case.sh
chmod +x ./06-select.sh
chmod +x ./07-function.sh
chmod +x ./demo_call.sh
运行 Shell 脚本
./01-helloworld.sh
./02-array.sh
./03-if.sh
./04-while.sh
./05-case.sh
./06-select.sh
./07-function.sh
helloworld.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 注意:"="号两边不能有空格,因为个人习惯问题,我就总喜欢在等号两边加上空格
demo="hello world"
# 在终端输出变量demo,也就是hello world
echo $demo
运行效果:

array.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 一对括号表示是数组,数组元素用“空格”符号分割开。
a=(1 2 3 4 5)
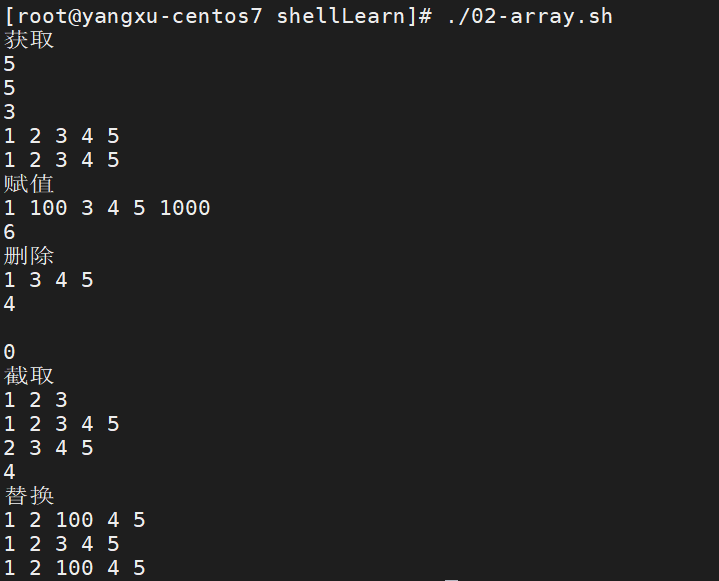
###### 获取 ######
echo "获取"
a=(1 2 3 4 5)
# 用${#数组名[@或*]} 可以得到数组长度
echo ${#a[@]}
echo ${#a[*]}
# 用${数组名[下标]} 可以得到指定下标的值,下标是从0开始
echo ${a[2]}
# 用${数组名[@或*]} 可以得到整个数组内容
echo ${a[@]}
echo ${a[*]}
###### 赋值 ######
echo "赋值"
a=(1 2 3 4 5)
# 直接通过 数组名[下标] 就可以对其进行引用赋值
a[1]=100
# 如果下标不存在,自动添加新一个数组元素
a[1000]=1000
echo ${a[*]}
echo ${#a[*]}
###### 删除 ######
echo "删除"
a=(1 2 3 4 5)
# unset 数组[下标] 可以清除相应的元素
unset a[1]
echo ${a[*]}
echo ${#a[*]}
# unset 数组[下标] 不带下标,清除整个数据。
unset a
echo ${a[*]}
echo ${#a[*]}
###### 截取 ######
echo "截取"
a=(1 2 3 4 5)
# 截取数组 ${数组名[@或*]:起始位置:长度},从下标0开始,截取长度为3,切片原先数组,返回是字符串,中间用“空格”分开
echo ${a[@]:0:3}
echo ${a[*]}
# 如果加上”()”,将得到切片数组,上面例子:c 就是一个新数据。
c=(${a[@]:1:4})
echo ${c[*]}
echo ${#c[*]}
###### 替换 ######
echo "替换"
a=(1 2 3 4 5)
# ${数组名[@或*]/查找字符/替换字符} 该操作不会改变原先数组内容,如果需要修改,可以看上面例子,重新定义数据。
echo ${a[@]/3/100}
echo ${a[@]}
# 如果需要修改,重新赋值给变量a
a=(${a[@]/3/100})
echo ${a[@]}
运行效果:
if.sh
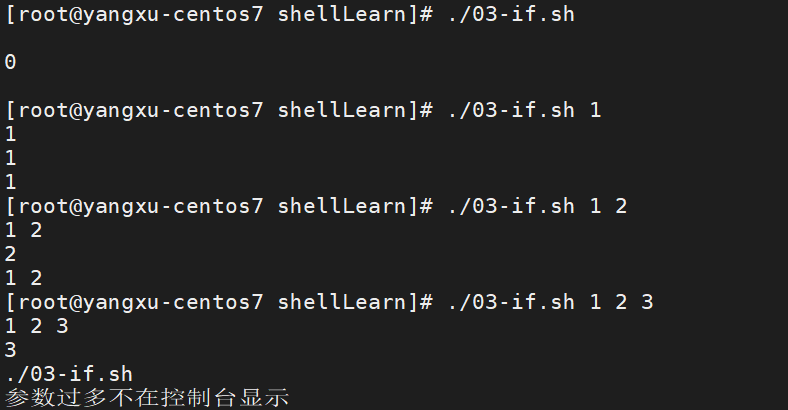
#!/bin/bash
# 打印终端命令行的所有参数
echo $*;
# 打印终端命令行的所有参数的个数
echo $#;
# 如果终端命令行的所有参数的个数小于3,就输出所有参数
if [ $# -lt 3 ]; then
echo $*;
else
echo $0;
echo "参数过多不在控制台显示";
fi
运行效果:
while.sh
#!/bin/bash
###### while循环例子1 ######
echo "while循环例子1";
i=10;
while [[ $i -gt 5 ]]; do
echo $i;
((i--));
done;
###### while循环例子2 ######
echo "while循环例子2";
# 循环读取/etc/hosts文件内容
while read line; do
echo $line;
done < /etc/hosts;
###### for循环例子1 ######
echo "for循环例子1";
for((i=1;i<=10;i++)); do
echo $i;
done;
###### for循环例子2 ######
echo "for循环例子2";
# seq 10 产生 1 2 3 。。。。10空格分隔字符串。
for i in $(seq 10); do
echo $i;
done;
###### for循环例子3 ######
echo "for循环例子3";
# 根据终端输入的文件名来检查当前目录该文件是否存在
for file in $*; do
if [ -f "$file" ]; then
echo "INFO: $file exists"
else
echo "ERROR: $file not exists"
fi
done;
###### until循环例子1 ######
echo "until循环例子1";
a=10;
until [[ $a -lt 0 ]]; do
echo $a;
((a--));
done;
运行效果:


case.sh
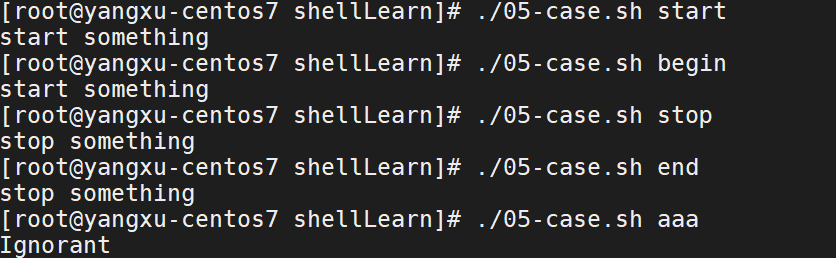
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
start | begin)
echo "start something"
;;
stop | end)
echo "stop something"
;;
*)
echo "Ignorant"
;;
esac
运行效果:
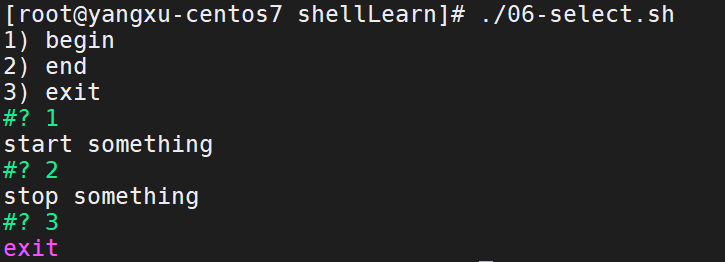
select.sh
#!/bin/bash
select ch in "begin" "end" "exit"; do
case $ch in
"begin")
echo "start something"
;;
"end")
echo "stop something"
;;
"exit")
echo "exit"
break;
;;
*)
echo "Ignorant"
;;
esac
done;
运行效果:
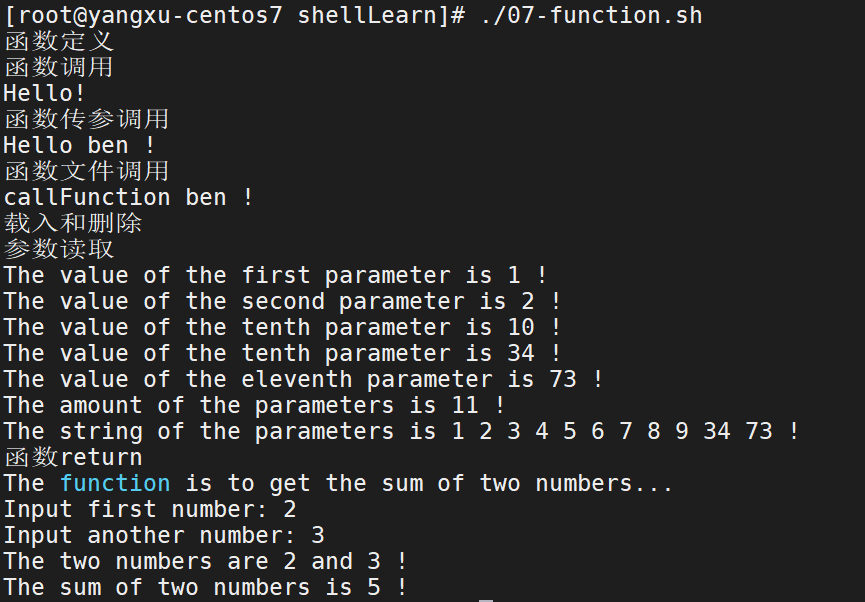
function.sh
#!/bin/bash
###### 函数定义 ######
echo "函数定义";
# 注意:所有函数在使用前必须定义。这意味着必须将函数放在脚本开始部分,直至shell解释器首次发现它时,才可以使用。调用函数仅使用其函数名即可。
function hello() {
echo "Hello!";
}
function hello_param() {
echo "Hello $1 !";
}
###### 函数调用 ######
# 函数调用
echo "函数调用";
hello;
###### 参数传递 ######
echo "函数传参调用";
hello_param ben;
###### 函数文件 ######
echo "函数文件调用";
# 调用(包含)函数文件,点和demo_call之间有个空格
. demo_call.sh;
# 调用函数
callFunction ben;
###### 载入和删除 ######
echo "载入和删除";
# 用unset functionname 取消载入
# unset callFunction;
# 因为已经取消载入,所以会出错
# callFunction ben;
###### 参数读取 ######
echo "参数读取";
# 参数读取的方式和终端读取参数的方式一样
# 注意:$10不能获取第10个参数,因为当n>=10时候,要用$(n)来获取参数。
funWithParam(){
echo "The value of the first parameter is $1 !"
echo "The value of the second parameter is $2 !"
echo "The value of the tenth parameter is $10 !"
echo "The value of the tenth parameter is ${10} !"
echo "The value of the eleventh parameter is ${11} !"
echo "The amount of the parameters is $# !"
echo "The string of the parameters is $* !"
}
funWithParam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 34 73
###### 函数return ######
echo "函数return";
funWithReturn(){
echo "The function is to get the sum of two numbers..."
echo -n "Input first number: "
read aNum
echo -n "Input another number: "
read anotherNum
echo "The two numbers are $aNum and $anotherNum !"
return $(($aNum+$anotherNum))
}
funWithReturn
# 函数返回值在调用该函数后通过 $? 来获得
echo "The sum of two numbers is $? !"
demo_call.sh
#!/bin/bash
function callFunction() {
echo "callFunction $1 !";
return 1;
}
运行效果:
Tomcat 部署脚本实例
deploy.sh
#!/bin/sh
war=$1
bin=$(cd `dirname $0`; pwd)
if [ ! -n "${war}" ]; then
echo "***Usage: $0 [project.war]"
exit 0
fi
if [ ! -f "${war}" ]; then
echo "***Error: ${war} does not exist."
exit 0
fi
if [ ! "${war##*.}" = "war" ]; then
echo "***Error: ${war} is not a war file."
exit 0
fi
echo "Deploy ${war##*/}..."
rm -rf ${bin}/../webapps/ROOT/ && unzip -qo ${war} -d ${bin}/../webapps/ROOT/
rm -rf ${bin}/../work/Catalina/localhost/
echo "Restart tomcat..."
exec ${bin}/restart.sh
restart.sh
#!/bin/sh
bin=$(cd `dirname $0`; pwd)
pid=$(ps aux | grep tomcat | grep -v grep | grep -v restart | grep ${bin} | awk '{print $2}')
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
echo "Shutdown..."
sh ${bin}/shutdown.sh
sleep 3
pid=$(ps aux | grep tomcat | grep -v grep | grep -v restart | grep ${bin} | awk '{print $2}')
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
kill -9 ${pid}
sleep 1
fi
fi
echo "Startup..."
sh ${bin}/startup.sh
if [ "$1" = "-v" ]; then
tail -f ${bin}/../logs/catalina.out
fi
将 deploy.sh 和 restart.sh 放到 apache-tomcat-8.5.57/bin/ 目录下。
赋予执行权限:
chmod +x ./deploy.sh
chmod +x ./restart.sh
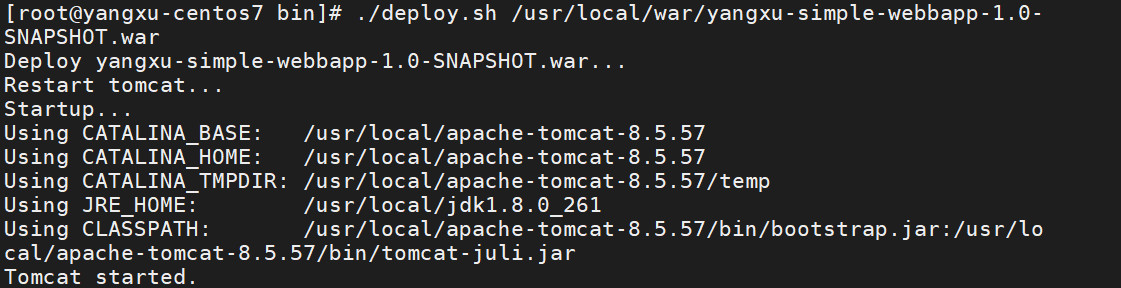
使用示例:
cd /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.57/bin/
./deploy.sh /usr/local/war/yangxu-simple-webbapp-1.0-SNAPSHOT.war
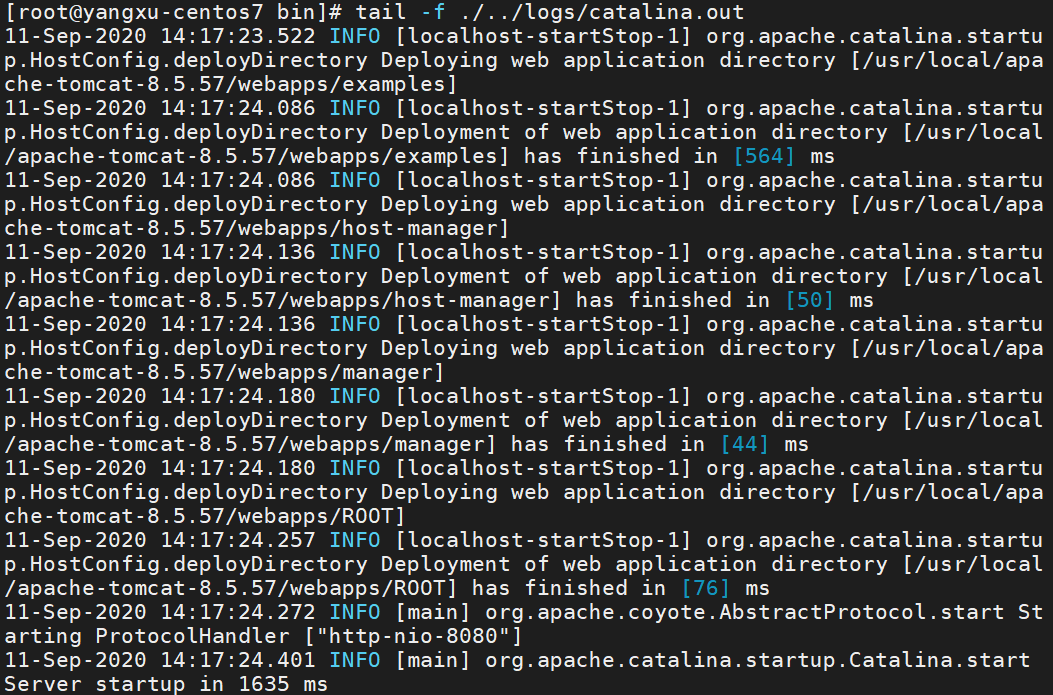
#查看启动日志
tail -f ./../logs/catalina.out