43.SpringBoot学习笔记–错误处理原理与定制错误页面
错误处理机制
Spring Boot 默认的错误处理机制
1、浏览器返回一个默认的错误页面;
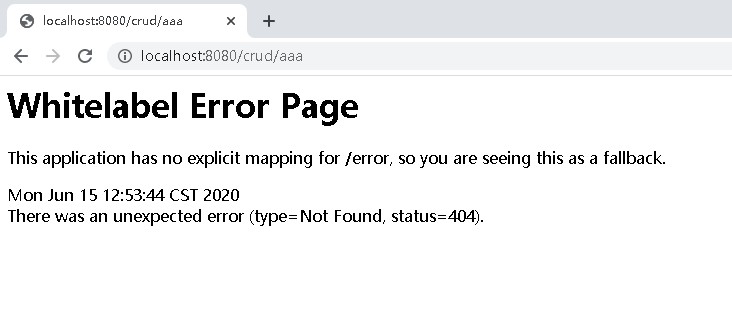
BasicErrorController 根据浏览器的请求头识别出是浏览器访问
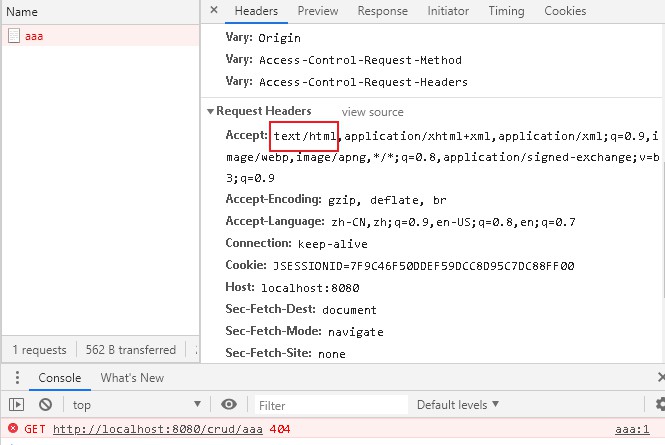
2、如果是其他客户端,默认响应一个 json 数据
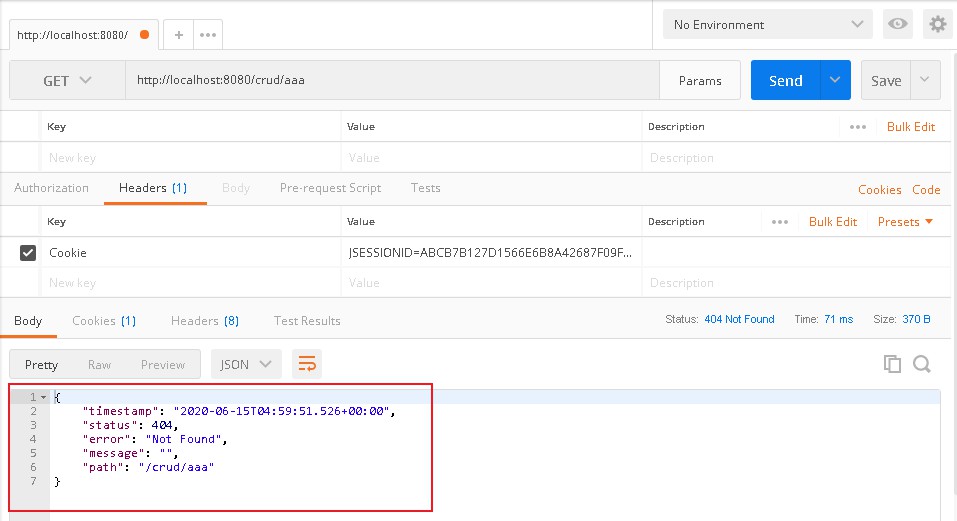
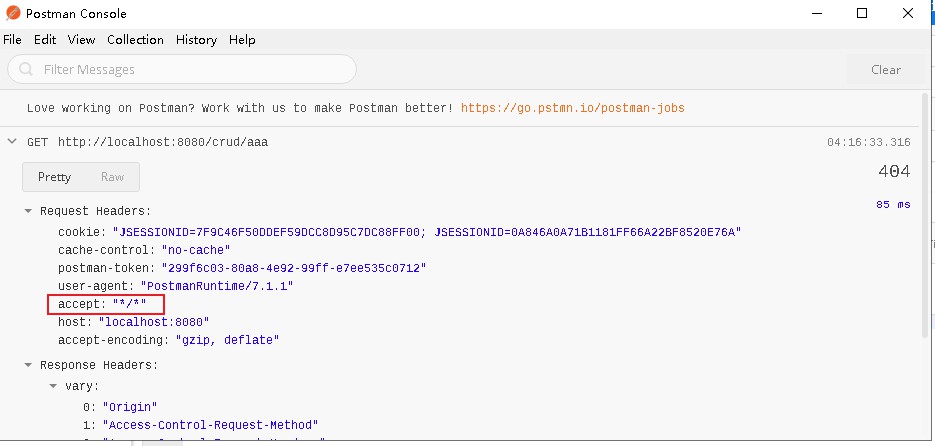
根据其他客户端发送的请求头识别出是非浏览器访问
原理:
一但系统出现 4xx 或者 5xx 之类的错误,ErrorPageCustomizer 就会生效(ErrorPageCustomizer),请求 /error,被 BasicErrorController 处理。
响应页面:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.AbstractErrorController#resolveErrorView
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
//所有的ErrorViewResolver得到ModelAndView
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
去哪个页面是由 DefaultErrorViewResolver 解析得到的。
参考:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
给容器中添加了以下组件
1、DefaultErrorAttributes:
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes#getErrorAttributes
帮我们在页面共享信息
@Override
@Deprecated
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest);
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace);
addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest);
return errorAttributes;
}
2、BasicErrorController:处理默认 /error 请求
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {}
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController#errorHtml
//产生html类型的数据,浏览器发送的请求,到这个方法处理
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面,包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
org.springframework.http.MediaType#TEXT_HTML_VALUE
/**
* A String equivalent of {@link MediaType#TEXT_HTML}.
*/
public static final String TEXT_HTML_VALUE = "text/html";
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController#error
////产生json数据,其他客户端到这个方法处理;
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(status);
}
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
3、ErrorPageCustomizer:
系统出现错误后,来到 error 请求进行处理(类似 web.xml 注册的错误页面规则)
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorProperties#path
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
4、DefaultErrorViewResolver:
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//默认SpringBoot可以去找到error/404这个页面
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
//如果模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址,就用模板引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,
this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
//模板引擎可用的情况下,返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//模板引擎不可用,就在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面,也就是error/404.html
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
定制错误处理机制
有模板引擎的情况下,将错误页面命名为 “错误状态码.html” 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的 error 文件夹下,也就是 error/状态码.html。 发生此状态码的错误就会来到对应的页面。
可以使用 4xx 和 5xx 作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误。在有精确的 “状态码.html” ,精确优先。
页面能获取的信息:
- timestamp:时间戳
- status:状态码
- error:错误提示
- exception:异常对象(经本人验证 Spring Boot v2.3.0 中无法获取)
- message:异常消息(经本人验证 Spring Boot v2.3.0 中无法获取)
- errors:JSR303 数据校验的错误都在这里(经本人验证 Spring Boot v2.3.0 中无法获取)
页面获取信息示例:
<h1>status: [[${status}]]</h1>
<h2>timestamp: [[${timestamp}]]</h2>
2、没有模板引擎,也就是模板引擎找不到这个错误页面,静态资源文件夹下找;
3、以上目录都找不到错误页面,就来到 Spring Boot 默认的错误提示页面。