31.SpringBoot学习笔记–SpringMVC自动配置原理
SpringMVC 自动配置
可以通过 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web 来了解 Web 的所有自动场景。
来自官网的说明:
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
- Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans. - Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).【静态资源文件夹路径,WebJars】
- Automatic registration of
Converter,GenericConverter, andFormatterbeans. - Support for
HttpMessageConverters(covered later in this document). - Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(covered later in this document). - Static
index.htmlsupport.【静态首页访问】 - Custom
Faviconsupport (covered later in this document). - Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (covered later in this document).
If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc.
If you want to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, and still keep the Spring Boot MVC customizations, you can declare a bean of type WebMvcRegistrations and use it to provide custom instances of those components.
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc, or alternatively add your own @Configuration-annotated DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration as described in the Javadoc of @EnableWebMvc.
参考:Spring MVC Auto-configuration
参考:Developing Web Applications
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
自动配置了 ViewResolver [视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发或是重定向到一个页面)]
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器。
定制视图解析器:可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器,ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 会自动将其组合进来。
参考的源码:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration.WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter#viewResolver
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager(beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// ContentNegotiatingViewResolver uses all the other view resolvers to locate
// a view so it should have a high precedence
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver;
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver#resolveViewName
@Override
@Nullable
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
RequestAttributes attrs = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
Assert.state(attrs instanceof ServletRequestAttributes, "No current ServletRequestAttributes");
List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes = getMediaTypes(((ServletRequestAttributes) attrs).getRequest());
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
List<View> candidateViews = getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
View bestView = getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
String mediaTypeInfo = logger.isDebugEnabled() && requestedMediaTypes != null ?
" given " + requestedMediaTypes.toString() : "";
if (this.useNotAcceptableStatusCode) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using 406 NOT_ACCEPTABLE" + mediaTypeInfo);
}
return NOT_ACCEPTABLE_VIEW;
}
else {
logger.debug("View remains unresolved" + mediaTypeInfo);
return null;
}
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver#getCandidateViews
private List<View> getCandidateViews(String viewName, Locale locale, List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes)
throws Exception {
List<View> candidateViews = new ArrayList<>();
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
Assert.state(this.contentNegotiationManager != null, "No ContentNegotiationManager set");
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
for (MediaType requestedMediaType : requestedMediaTypes) {
List<String> extensions = this.contentNegotiationManager.resolveFileExtensions(requestedMediaType);
for (String extension : extensions) {
String viewNameWithExtension = viewName + '.' + extension;
view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewNameWithExtension, locale);
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
}
}
}
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultViews)) {
candidateViews.addAll(this.defaultViews);
}
return candidateViews;
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver#initServletContext
@Override
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values();
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.size());
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : matchingBeans) {
if (this != viewResolver) {
this.viewResolvers.add(viewResolver);
}
}
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < this.viewResolvers.size(); i++) {
ViewResolver vr = this.viewResolvers.get(i);
if (matchingBeans.contains(vr)) {
continue;
}
String name = vr.getClass().getName() + i;
obtainApplicationContext().getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().initializeBean(vr, name);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.viewResolvers);
this.cnmFactoryBean.setServletContext(servletContext);
}
示例
Springboot04WebRestfulcrudApplication
package demo.yangxu.springboot;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot04WebRestfulcrudApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot04WebRestfulcrudApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ViewResolver myViewReolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver {
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}
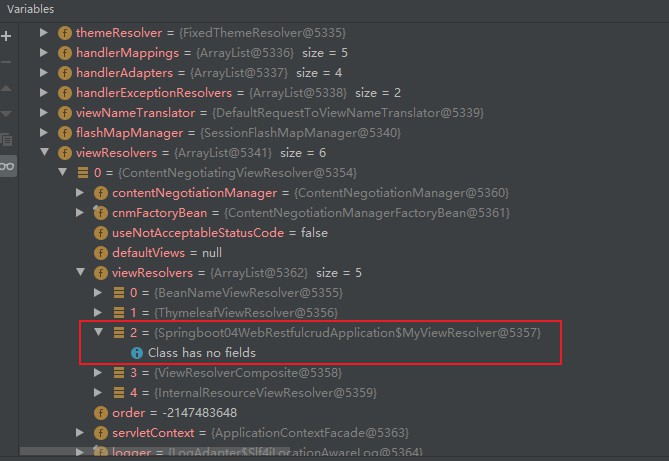
找到 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet,在 doDispatch() 所在行设置断点,启动项目后访问一个请求,可以在 this -> viewResolvers -> ContentNegotiationViewResolver -> viewResolvers 中找到定制的视图解析器 MyViewResolver
Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
Converter:转换器。做类型转换的,或者数据格式化处理。可以把数据在送到 Controller 之前做处理,变成需要的格式或者类型。Converter 是一种类型转换另一种,可以用在很多层中。
例如 Controller 中有一个方法 public String hello(User user),页面带来的数据跟 User 对象的属性一一对应,SpringMVC 会自动封装,在自动封装期间会出现类型转换问题。例如页面提交的 18 是一个文本类型,需要转换为 Integer 类型;或者页面提交的 true 是一个文本类型,需要转换为 Boolean 类型。这种需要类型转换的场景需要使用 Converter 组件。
Formatter:格式化器。是 String 转换另一种,适用于 Web 层,SpringMVC 程序中推荐使用。例如将 2017.12.17 字符串类型转换为 Date 类型。
自己添加的格式化器转换器,只需要放在容器中即可。
Support for HttpMessageConverters
HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC 用来转换 Http 请求和响应的。例如将 User 转换为 JSON。
HttpMessageConverters 从容器中确定,获取所有的HttpMessageConverter。
自己给容器中添加 HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)
If you need to add or customize converters, you can use Spring Boot’s HttpMessageConverters class, as shown in the following listing:
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConverters;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.http.converter.*;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters customConverters() {
HttpMessageConverter<?> additional = ...
HttpMessageConverter<?> another = ...
return new HttpMessageConverters(additional, another);
}
}
Any HttpMessageConverter bean that is present in the context is added to the list of converters. You can also override default converters in the same way.
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver
定义错误代码生成规则。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration.WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter#getMessageCodesResolver
@Override
public MessageCodesResolver getMessageCodesResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties.getMessageCodesResolverFormat() != null) {
DefaultMessageCodesResolver resolver = new DefaultMessageCodesResolver();
resolver.setMessageCodeFormatter(this.mvcProperties.getMessageCodesResolverFormat());
return resolver;
}
return null;
}
org.springframework.validation.DefaultMessageCodesResolver.Format
/**
* Common message code formats.
* @see MessageCodeFormatter
* @see DefaultMessageCodesResolver#setMessageCodeFormatter(MessageCodeFormatter)
*/
public enum Format implements MessageCodeFormatter {
/**
* Prefix the error code at the beginning of the generated message code. e.g.:
* {@code errorCode + "." + object name + "." + field}
*/
PREFIX_ERROR_CODE {
@Override
public String format(String errorCode, @Nullable String objectName, @Nullable String field) {
return toDelimitedString(errorCode, objectName, field);
}
},
/**
* Postfix the error code at the end of the generated message code. e.g.:
* {@code object name + "." + field + "." + errorCode}
*/
POSTFIX_ERROR_CODE {
@Override
public String format(String errorCode, @Nullable String objectName, @Nullable String field) {
return toDelimitedString(objectName, field, errorCode);
}
};
/**
* Concatenate the given elements, delimiting each with
* {@link DefaultMessageCodesResolver#CODE_SEPARATOR}, skipping zero-length or
* null elements altogether.
*/
public static String toDelimitedString(String... elements) {
StringJoiner rtn = new StringJoiner(CODE_SEPARATOR);
for (String element : elements) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(element)) {
rtn.add(element);
}
}
return rtn.toString();
}
}
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean
用于初始化 WebDataBinder,WebDataBinder的功能是把请求数据绑定到 JavaBean 中。
可以自己配置一个 ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer 来替换默认的。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration#getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
@Override
protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, Validator mvcValidator) {
try {
return this.beanFactory.getBean(ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer.class);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
return super.getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(mvcConversionService, mvcValidator);
}
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport#getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
/**
* Return the {@link ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer} to use for
* initializing all {@link WebDataBinder} instances.
*/
protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, Validator mvcValidator) {
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer initializer = new ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer();
initializer.setConversionService(mvcConversionService);
initializer.setValidator(mvcValidator);
MessageCodesResolver messageCodesResolver = getMessageCodesResolver();
if (messageCodesResolver != null) {
initializer.setMessageCodesResolver(messageCodesResolver);
}
return initializer;
}
org.springframework.web.bind.support.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer#initBinder
@Override
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(this.autoGrowNestedPaths);
if (this.directFieldAccess) {
binder.initDirectFieldAccess();
}
if (this.messageCodesResolver != null) {
binder.setMessageCodesResolver(this.messageCodesResolver);
}
if (this.bindingErrorProcessor != null) {
binder.setBindingErrorProcessor(this.bindingErrorProcessor);
}
if (this.validator != null && binder.getTarget() != null &&
this.validator.supports(binder.getTarget().getClass())) {
binder.setValidator(this.validator);
}
if (this.conversionService != null) {
binder.setConversionService(this.conversionService);
}
if (this.propertyEditorRegistrars != null) {
for (PropertyEditorRegistrar propertyEditorRegistrar : this.propertyEditorRegistrars) {
propertyEditorRegistrar.registerCustomEditors(binder);
}
}
}
修改 Spring Boot 的默认配置
模式:
1、Spring Boot 在自动配置组件时,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component),如果有就使用用户配置的,如果没有,就自动配置。如果有些组件可以有多个(如:ViewResolver),将用户配置的和默认的组合起来;
2、在 Spring Boot 中有很多的 xxxConfigurer 进行扩展配置;
3、在 Spring Boot 中有很多的 xxxCustomizer 进行定制配置。